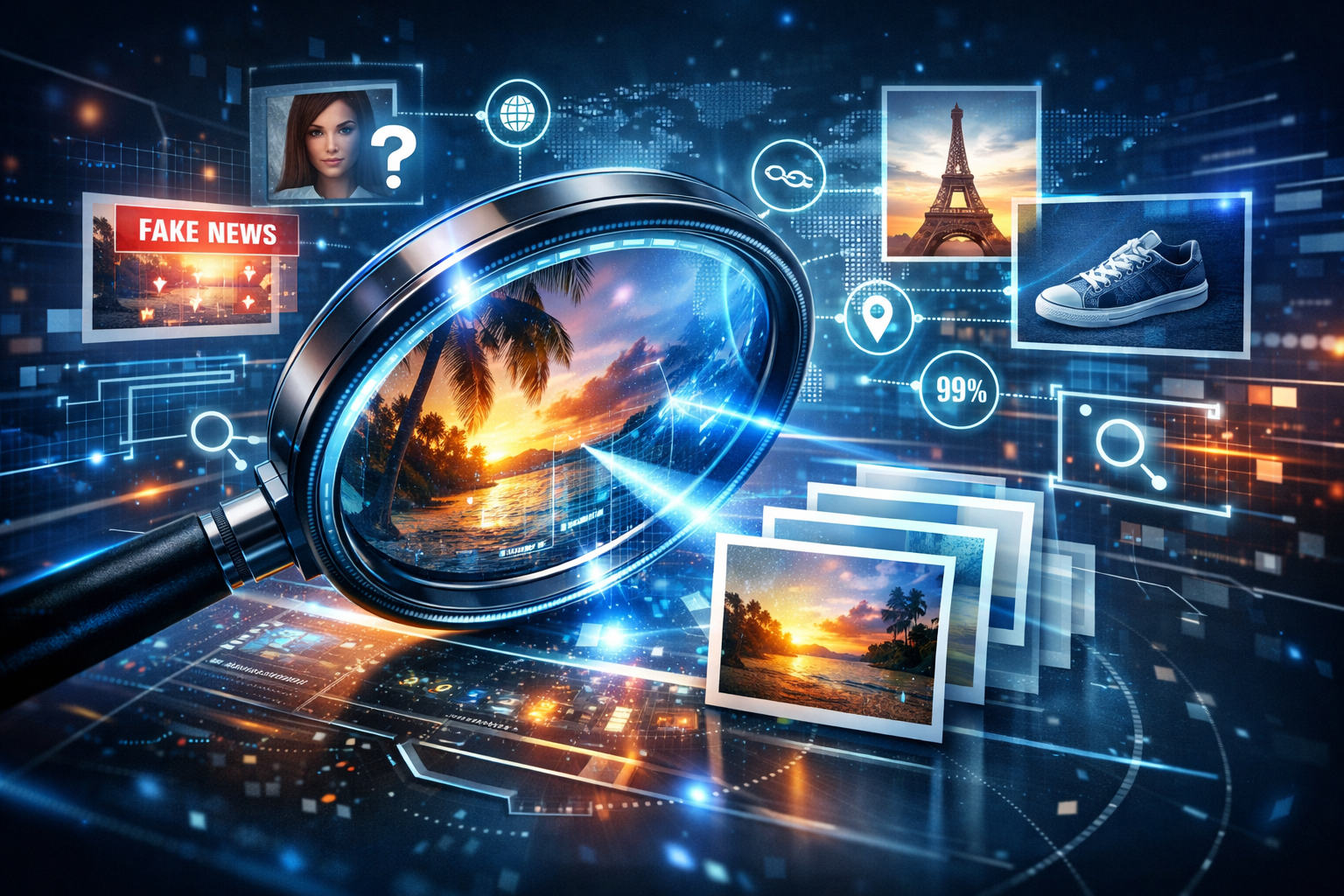
Reverse Image Search Scroll through any social feed today and you’ll see it: a nonstop flood of images. Memes, product shots, news photos, travel snaps, AI art—pictures are now one of the main ways we share ideas and make decisions online.
But there’s a problem.
Where did that image really come from? Is it real or edited? Who owns it? Has it been used in a scam? Or maybe you just want the same image in higher quality.
That’s exactly where reverse image search comes in. Think of it as a search engine that works backwards—you feed it a picture, and it goes hunting across the web to tell you what it can find.
In this complete guide, we’ll walk through what reverse image search is, how it works, the best tools to use, how to run searches on desktop and mobile, and the smartest ways to use it in real life.
What Is Reverse Image Search?
Reverse image search is a way to search the internet using an image instead of text.
Instead of typing “red sneakers brand” into a search box, you:
-
Upload a photo of the sneakers
-
Or paste the URL of an image you found online
The tool then scans the web for:
-
Exact matches
-
Visually similar images
-
Pages where the image appears
This is useful when:
-
You don’t know what to type into a normal search bar
-
You want to verify where an image came from
-
You need more context behind a viral picture
In simple terms, reverse image search helps you answer:
“Where has this picture been used, and what’s the story behind it?”
How Does Reverse Image Search Work?
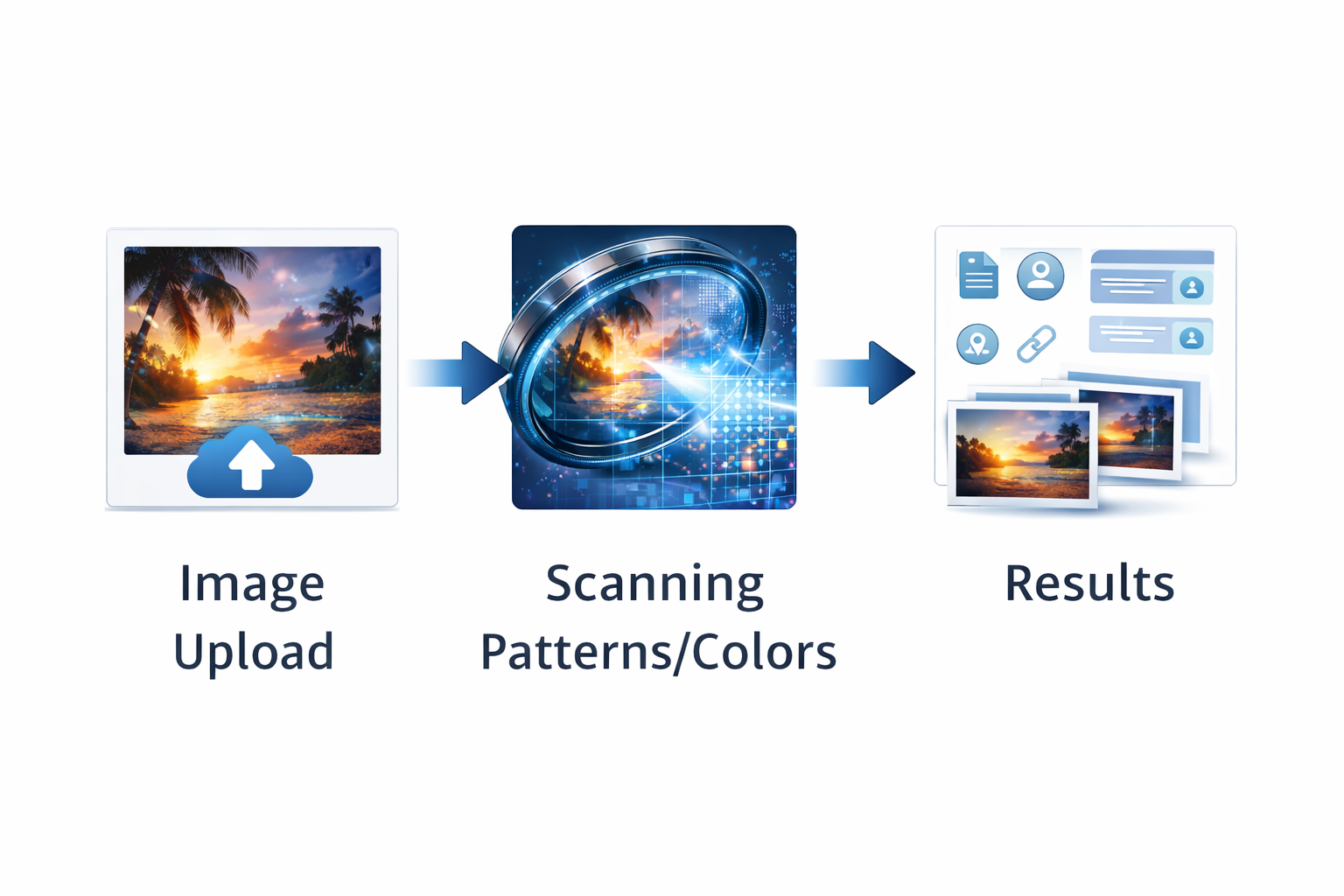
Let’s walk through what happens behind the scenes when you upload a photo.
-
You submit the image
You either upload a file from your device or paste an image URL into a reverse image search tool. -
The system analyzes the image itself
It doesn’t care about the file name. Instead, it studies:
-
Colors
-
Shapes
-
Textures
-
Edges and lines
-
Objects, faces, and visual patterns
-
-
It converts the image into a “visual signature”
This is like a mathematical fingerprint for the photo. -
It compares that signature to a huge database
The tool matches your image against billions of images stored online.
Thanks to advanced computer vision and AI, this comparison happens in seconds. -
You get a list of matches and similar images
Results may include:-
Exact copies
-
Cropped or resized versions
-
Edited or filtered variations
-
Visually similar images
-
Over time, the algorithms behind these tools keep learning and improving. That means:
-
Better recognition of complex patterns
-
More accurate matches
-
Faster, more user-friendly results
You don’t need to be a tech expert to use it. The heavy lifting happens behind the scenes.
Popular Reverse Image Search Tools
There isn’t just one reverse image tool. Different platforms specialize in different strengths—some are great for general web use, others for faces, products, or regional content.
Below are the main tools you should know.
Google Images Reverse Search
![]()
Google Images is the most widely used reverse image search engine.
How it works:
-
Go to Google Images
-
Click the camera icon (on desktop)
-
Upload an image or paste an image URL
-
View visually similar images and web pages using that image
Why people love it:
-
Massive image index
-
Fast results
-
Good at finding pages that reuse the same photo
-
Helpful for general verification and sourcing
If you only use one tool, Google Images is usually the best starting point.
Lenso.ai – Advanced Face & Reverse Image Search
Lenso.ai focuses strongly on facial recognition and deep reverse image search.
You can upload an image and explore categories like:
-
People
-
Duplicates (for copyright and near-identical images)
-
Places
-
Related
-
Similar
With Lenso, you can find:
-
Old photos of yourself that appear online
-
Where your photos are being used on the internet
-
Possible copyright violations
-
Potential catfish or fraud profiles
-
Possible romance scammers using stolen pictures
You can also:
-
Filter results by keyword or domain
-
Sort by newest, oldest, best, or worst match
-
Set a free alert if there are no current matches—Lenso will notify you when future matches appear
It’s particularly useful when your main concern is faces, identity, and copyright.
Bing Visual Search
Bing Visual Search is Microsoft’s visual search engine.
It’s strong at:
-
Recognizing objects, products, and landmarks
-
Identifying items inside a larger image (like a handbag in a street photo)
-
Providing product information, similar items, or where to buy something
Users appreciate that Bing often picks up smaller details that other tools might ignore, which can be handy when you’re trying to identify a specific object in a complex picture.
TinEye Reverse Image Search
TinEye is one of the original specialized reverse image search engines.
What it does best:
-
Tracks where an image first appeared
-
Finds exact or near-exact matches, even when the image has been resized, rotated, or slightly edited
-
Shows how an image has been altered or reused over time
This makes TinEye very popular with:
-
Photographers
-
Designers
-
Brands
-
Anyone who wants to monitor how their images are used online
It’s a great tool for copyright protection and image tracking.
Yandex Reverse Image Search
Yandex is a major search engine in Russia and surrounding regions, and its image search is surprisingly powerful.
Key strengths:
-
Strong facial recognition
-
Excellent at finding lookalike locations, art, and objects
-
Often discovers sources that Google or Bing miss, especially in certain regions
Because its index covers different parts of the web, Yandex can sometimes give you a broader, more global picture of how and where an image appears online.
Mobile Apps & Browser Extensions
Reverse image search has also moved into:
-
Mobile apps: Many apps let you reverse search directly from your camera or photo gallery. Helpful when you’re out and about and want to know more about something you’ve just snapped.
-
Browser extensions: Extensions let you right-click any image on a webpage and instantly run a reverse search across multiple engines.
These shortcuts save time, especially if you use reverse image search regularly.
How to Do a Reverse Image Search (Step by Step)
Let’s keep this practical. Here’s a simple process you can use with most tools.
Basic steps:
-
Choose a tool
For example, Google Images, Lenso.ai, Bing Visual Search, TinEye, or Yandex. -
Upload an image or paste a URL
-
Upload from your device
-
Or right-click and copy the image address
-
Or drag and drop into the search box (desktop)
-
-
Wait while the tool analyzes the image
This usually takes just a couple of seconds. -
Review the results
You’ll see:-
Exact matches
-
Visually similar images
-
Web pages where the image appears
-
-
Explore relevant links
Click through to:-
Find the original source
-
Get context (article, caption, date, location)
-
Check how the image has been used
-
-
Repeat on another tool if needed
If results are weak, try another engine like Yandex or Lenso.ai for a different angle.
Reverse Image Search on Social Platforms
Social media is a major source of images—and misinformation. While platforms like Facebook and Instagram don’t offer native reverse image search, you can still investigate what’s circulating.
Here’s how it usually works across platforms.
Reddit Reverse Image Search
Reddit is full of reposts, memes, and viral photos.
You can:
-
Download or copy the image
-
Run it through a reverse image search tool
-
Find other Reddit threads where it was posted
-
See original posts, timestamps, and community discussions
This is great for finding context, especially around viral or controversial images.
Facebook Reverse Image Search
Facebook doesn’t let you search by image directly.
Instead, you can:
-
Upload the image to a reverse search engine
-
See if it appears on public Facebook profiles or pages (if they’re indexed)
-
Spot repeated use of identical profile pictures across different names
This helps with:
-
Identity checks
-
Detecting fake accounts
-
Investigating misleading posts that reuse photos
Instagram Reverse Image Search
Instagram also doesn’t have built-in image search.
The workaround:
-
Screenshot or download the image (respecting copyright and privacy)
-
Use a reverse image tool to search the web
-
See if the photo appears on other sites or public Instagram accounts
This can reveal:
-
Original photographers or creators
-
Reposted or stolen content
-
Fake “influencer” accounts using someone else’s images
iPhone Reverse Image Search
On an iPhone, you’ve got a couple of easy options:
-
Safari (desktop site mode)
-
Open Safari
-
Go to Google Images and request the desktop site
-
Use the camera icon to upload a photo
-
-
From the Photos app (via Share)
-
Open the photo
-
Tap Share
-
Use a browser or app integration that supports image search
-
It’s quick, and handy for identifying objects, locations, or verifying an image you’ve saved.
Face Reverse Image Search
Face reverse search lets you upload a portrait or profile photo to find:
-
Similar images
-
Related profiles
-
Appearances on websites or news pages
It’s commonly used for:
-
Checking if a profile photo is stolen
-
Investigating romance scams or catfishing
-
Verifying whether a person’s images appear in other contexts
Tools like Lenso.ai and some search engines are designed specifically with facial matching in mind.
AI Reverse Image Search
Modern AI reverse image search goes further than traditional methods.
With AI, tools can:
-
Understand shapes, colors, and objects more accurately
-
Recognize scenes and concepts (e.g., “beach sunset”, “running shoes”, “city skyline”)
-
Detect common edits and manipulations
-
Provide smarter, more context-aware matches
This leads to:
-
Better identification of objects and places
-
More precise verification of image authenticity
-
Stronger detection of altered images or deepfakes
AI is what’s pushing visual search into its next generation.
Top Use Cases for Reverse Image Search

So, where does all of this actually help you in real life? Let’s break down the most powerful uses.
1. Verifying if a Photo Is Real
We’ve all seen shocking pictures online—storms, disasters, “breaking news”, celebrity scandals. Many of them are:
-
Edited
-
Taken out of context
-
Many years old but presented as recent
With reverse image search, you can:
-
See when the image first appeared
-
Find original articles or sources
-
Check if it’s been used in other stories
This is crucial for:
-
Journalists
-
Fact-checkers
-
Anyone who doesn’t want to share misinformation
2. Tracking Image Copyright & Ownership
If you’re a:
-
Artist
-
Designer
-
Brand
your images are valuable. Reverse image search lets you:
-
See where your work appears online
-
Discover unauthorized usage
-
Decide whether to request credit, ask for removal, or issue legal notices
It’s one of the simplest ways to protect your visual content.
3. Identifying Objects, Products & Places
Ever seen:
-
A cool lamp you want to buy?
-
A building you’d like to visit?
-
A plant or dog breed you couldn’t name?
Instead of guessing keywords, you can:
-
Upload the image
-
Let the tool identify or suggest what it is
-
Find product pages, similar items, or location info
It’s like pointing your phone at the world and asking, “What’s this?”
4. Finding Higher-Resolution Versions of an Image
Sometimes you have a tiny, blurry version of a great picture.
Reverse image search can:
-
Locate larger or higher-quality versions
-
Help you find the original upload instead of a compressed copy
This is especially handy for:
-
Presentations
-
Blog posts or reports
-
Personal projects where quality matters
5. Detecting Fake Profiles, Scams & Catfishing
Scammers often:
-
Steal photos from real people
-
Use stock images as profile pictures
-
Recycle the same photo across multiple fake accounts
Running a reverse image search on a suspicious profile picture can show:
-
The same face used under different names
-
Images taken from modelling websites or real users
-
Red flags that suggest fraud or catfishing
It’s a simple, powerful way to protect yourself online.
Advanced Tips & Best Practices
Want better results? Try these simple tweaks:
-
Use clear, sharp images
Blurry or tiny photos are harder to match. -
Crop to the main subject
If the photo has lots of elements, crop in on the person, product, or object you actually care about. -
Test more than one tool
Google, Yandex, Lenso.ai, Bing, and TinEye each have different strengths. -
Save important links and sources
If you’re doing research or investigations, keep a record of useful results. -
Try both upload and URL methods
Some images behave differently depending on how you submit them.
Limitations of Reverse Image Search
As powerful as it is, reverse image search isn’t perfect. Here’s what it can’t always do:
-
Find non-indexed images
If an image lives behind a login or in a private account, it won’t show up. -
Handle heavily edited images perfectly
Extreme edits, filters, or composites can make matching harder. -
Index brand-new images instantly
Very recent uploads might not appear in search results yet. -
Access private social media content
Only public pages and profiles that search engines can crawl will be visible. -
Work well with low-quality images
Tiny, dark, or distorted photos reduce accuracy.
Knowing these limits helps you interpret results more realistically.
The Future of Reverse Image Search Technology
Reverse image search is evolving fast—and AI is the main driver.
Here’s what we can expect:
-
Smarter understanding of context
Tools won’t just find matching pixels; they’ll explain what’s happening in the image and why it matters. -
Better detection of edited or fake content
Systems will get better at spotting manipulations, deepfakes, and subtle edits. -
Richer visual histories
You’ll be able to see not just where an image appears now, but how it has changed and spread over time. -
Deeper mobile integration
More apps will build visual search into cameras, galleries, and browsers as a default feature.
Put simply, we’re heading toward a world where you can point your device at almost anything and get trusted, detailed information instantly.
Conclusion
In a world where images travel faster than facts, reverse image search has quietly become one of the most important tools for digital literacy. It helps you cut through noise, question what you see, and make decisions based on reality, not just appearances.
Whether you’re a casual internet user, a brand, a creator, or a researcher, learning how to use reverse image search effectively is like learning how to read in a visual internet. Once you’ve tried it a few times, you’ll wonder how you ever surfed the web without it.