Image Search Techniques are the real language of the internet. Scroll through any social feed, product page, or news site, and you’ll notice one thing: visuals do most of the talking. We use pictures to learn, to compare, to decide, and to judge whether something feels trustworthy or not.
In a world where content moves fast and attention spans are short, knowing how to search with images has become just as important as knowing how to search with words. That’s where image search techniques step in.
Whether you’re a student, marketer, journalist, designer, photographer, or just curious about something you’ve seen online, understanding image search can save you time, prevent mistakes, and unlock a lot of useful information you’d miss otherwise.
In this guide, we’ll walk through what image search actually is, how it works behind the scenes, the main techniques you can use, the best tools on the web, common mistakes to avoid, and where all of this is headed in the future.
What Is Image Search Techniques?
Let’s start simple: Image Search Techniques is the process of finding images online that match either:
-
A text query (keywords you type), or
-
A visual query (an image you upload or link to)
So instead of only typing something like “blue running shoes with white sole,” you can:
-
Use text to find images that match that description
-
Or upload a picture of the shoes you like and let the search engine find similar options
Image search helps you:
-
Find the original creator of a photo
-
Identify a product you saw in a post or ad
-
Check whether an image has been edited or taken out of context
-
Discover similar visuals for inspiration or comparison
It’s especially powerful in areas where visual accuracy and authenticity matter, like:
-
Journalism and fact‑checking
-
Digital marketing and branding
-
eCommerce and product discovery
-
Design and creative work
Over time, image search has evolved from simple keyword matching to something much smarter. Thanks to AI and machine learning, search engines now analyze the content, structure, and context of images — not just the text around them.
How Does Image Search Techniques Work?
Behind every quick image result is a lot of complex technology: AI, machine learning, and computer vision.
Here’s the process, broken down in plain language.
1. You Provide a Query
You either:
-
Type a keyword or phrase, or
-
Upload an image file, or
-
Paste an image URL
2. The System Analyzes the Input
For text‑based image search, the engine looks at:
-
Image titles
-
Alt text
-
Page content around the image
-
Tags or labels added by creators
For visual (image‑based) search, the engine breaks the image into key visual components, such as:
-
Colors
-
Textures
-
Edges and contours
-
Shapes and patterns
-
Objects and faces
It essentially converts the image into a kind of visual fingerprint.
3. Matching Against a Huge Image Index
The search engine then compares your query (text or image fingerprint) against billions of images in its index.
It looks for:
-
Direct matches
-
Near‑identical variations (cropped, resized, slightly edited)
-
Visually similar content
-
Related pages where the image appears
4. Ranking and Displaying Results
The system ranks results based on relevance and context. For visual search, this includes:
-
How closely the visuals match
-
Whether the image appears on authoritative or popular sites
-
How frequently similar images appear
For example:
-
If you upload a photo of a red handbag, the engine identifies that it’s a bag, notes its color and shape, then shows you similar handbags from online stores, blogs, or marketplaces.
-
If you upload a picture of a famous landmark, it recognizes the building or landscape and returns results with location information, travel guides, or historical details.
In short, image search blends what’s in the picture with what’s written about it online.
Main Types of Image Search Techniques
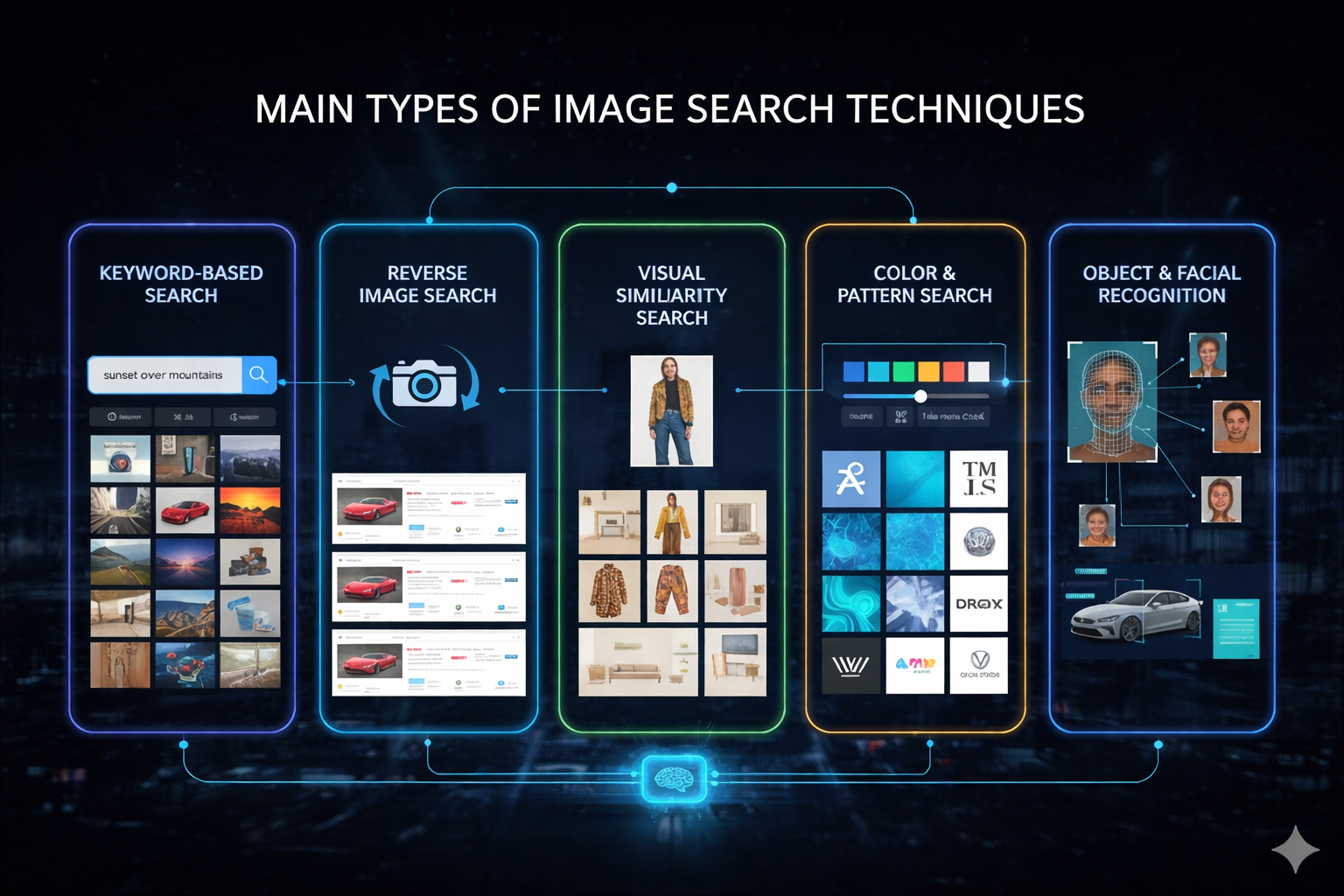
Not all image searches are the same. Different goals call for different Image Search Techniques . Let’s break down the main ones you’ll use.
Keyword-Based Image Search
This is the classic, easiest method most people already use.
You:
-
Type descriptive keywords (for example, “sunset over snow‑capped mountains” or “minimalist business icons”)
-
Hit search
-
Browse through a grid of images that match your description
This method relies heavily on metadata:
-
Image title
-
Alt text
-
Caption
-
Tags
-
Page content
Best for:
-
General, concept‑level search
-
Stock‑like images (nature, backgrounds, icons, generic product visual)
-
Cases where you already know how to describe what you need in word
If your keywords are clear and specific, keyword‑based image search can be surprisingly effective.
Reverse Image Search
Reverse image search flips the usual flow: instead of using text to find images, you use an image to find more information about it.
You:
-
Upload an image (or paste its URL)
-
Let the engine scan the web for:
-
Exact matches
-
Cropped or resized version
-
Slightly edited copy
-
Pages that contain that image
-
Use cases:
-
Finding the original source of a photo
-
Checking if your image has been reused without permission
-
Tracking plagiarism or content theft
-
Investigating fake news or misleading visuals
-
Seeing how widely a particular image has spread online
Reverse image search is one of the most powerful tools for verification and copyright protection.
Visual Similarity Search
Reverse image search looks for the same or near‑identical images. Visual similarity search looks instead for images that look alike aesthetically.
It detects similarities in:
-
Layout and composition
-
Patterns and textures
-
Colors and tones
-
Overall style
Where it shines:
-
Fashion: finding clothes that look like a design you love
-
Interior design: discovering similar furniture or decor pieces
-
eCommerce: suggesting visually similar products
-
Inspiration: turning a single image into a moodboard of related visuals
Think of it as saying to the search engine: “Show me more things with this style.”
Color and Pattern-Based Search
Sometimes what matters most in an image is the color palette or pattern, not the specific object.
Color & pattern‑based search allows you to:
-
Filter images by specific colors or gradients
-
Find visuals that fit a brand’s color system or campaign theme
-
Maintain visual consistency across creative work
Who uses it most:
-
Designers and art directors
-
Brand managers
-
Advertisers and creative teams
Many image platforms and search tools offer color filters so you can narrow your results to, say, “blue tones only” or “warm neutrals,” which is incredibly useful in design‑driven projects.
Object and Facial Recognition Search
This is where computer vision gets very smart.
-
Object recognition identifies specific items in an image:
-
Cars, animals, furniture, tools, devices, logos, and more
-
-
Facial recognition identifies or matches human faces (within legal and ethical limits).
These tools are used by:
-
Law enforcement agencies
-
Media organizations
-
Security and verification platforms
-
Social media networks
Examples:
-
Matching whether the same person appears in different photos
-
Identifying logos used without permission
-
Recognizing specific vehicle models or products
-
Reading handwriting or text within images using OCR (optical character recognition)
These techniques make image search far more precise and useful for tasks involving identity, authenticity, and detailed analysis.
When Should You Use Each Image Search Technique?
Picking the right approach is crucial if you want fast, accurate results.
- Use keyword-based search when:
-
-
You need general visuals or concept images
-
You can describe what you want clearly in words
-
-
Use reverse image search when:
-
You already have an image and want to find:
-
The source
-
Other usage
-
Possible manipulations
-
-
-
Use visual similarity search when:
-
Style, look, and aesthetic matter more than exact matches
-
You’re shopping, designing, or collecting inspiration
-
-
Use color/pattern search when:
-
You’re building a brand‑consistent visual library
-
Matching specific campaign or design palettes
-
-
Use object/facial recognition when:
-
Identification, analysis, or verification is key
-
You’re investigating, fact‑checking, or tracking specific people, logos, or items
-
You can also combine techniques. For example:
-
A marketer might start with keyword search to generate ideas, then use reverse image search to check where a specific image comes from and whether it’s safe to use.
Understanding each method’s strength is the quickest route to better results.
Top Image Search Tools You Should Know
You don’t have to build this tech yourself. There are powerful tools already available — many of them free or freemium.
Here are some of the most useful platforms for different types of image search.
Google Images – The Standard for Keyword & Reverse Search
Google Images is still the most widely used starting point.
You can:
-
Type keywords for classic image search
-
Click the camera icon to upload an image or paste a URL
-
Get visually similar images and pages containing that image
Key strengths:
-
Massive index of images from all over the web
-
Smart algorithms for relevance
-
Good at both keyword and reverse image search
-
Fast, reliable results for both personal and professional use
If you only use one tool, Google Images is usually your first stop.
Lenso AI – Best for Face Search & AI‑Powered Reverse Image Search
Lenso.ai specializes in reverse image search with a strong focus on faces and identity.
With Lenso AI, you can:
-
Upload an image and find where similar or identical images appear online
-
Check if your images are being reused without permission
-
Detect potential catfishing, impersonation, or fraud
-
Identify stolen content or misuse of your personal photos
-
Detect exact duplicates of a given image
Extra features:
-
Filtering and sorting options (by relevance, date, etc.)
-
Alerts that notify you when new matches for an image appear online
If you’re concerned about privacy, reputation, or image misuse, Lenso AI is incredibly valuable.
TinEye – Best for Tracking Origins and Duplicates
TinEye is a dedicated reverse image search engine.
What it does well:
-
Finds where an image first appeared or where else it’s used
-
Detects edited, cropped, or resized versions
-
Tracks image usage over time
Who loves it:
-
Journalists checking authenticity
-
Photographers and artists monitoring their work
-
Brands tracking unauthorized use of their visuals
If your main goal is image tracking and copyright protection, TinEye is a strong choice.
Bing Visual Search – Great for Shopping & Objects
Bing Visual Search puts object‑level search front and center.
You can:
-
Highlight a specific part of an image (like shoes, a bag, or a lamp)
-
Ask Bing to find visually similar products or items
Why it’s popular:
-
Excellent for online shopping and style matching
-
Integrated into Microsoft Edge, making visual search easy while browsing
It’s especially handy if you often see items in photos and think, “Where can I buy that?”
Pinterest Lens – Perfect for Lifestyle, Fashion & Décor
Pinterest Lens turns everyday images into inspiration.
With Lens, you can:
-
Take a photo or upload one
-
Discover similar outfits, room setups, recipes, and DIY projects
-
Explore ideas visually instead of searching by text
Best for:
-
Lifestyle creators and influencers
-
Fashion lovers
-
Home decor enthusiasts
-
Anyone building moodboards or getting visual ideas
It’s less about verification and more about creative discovery.
Yandex Images – Strong Global Reverse Image Recognition
Yandex Images is part of Russia’s largest search engine and is well known worldwide for its image recognition.
Strengths:
-
Excellent at finding faces, objects, and landmarks
-
Often returns results that Google or Bing miss, especially in certain regions
-
Highly valued by professionals running deeper visual investigations
Many people use Yandex to confirm or expand on results they got from other engines.
Shutterstock – Ideal for Copyright Protection & Tracking
Shutterstock is primarily a stock photo platform, but it also offers a reverse image feature for registered users.
You can:
-
Check where your licensed images may be appearing
-
Identify potential misuse of your stock photos
-
Protect your intellectual property
For brands and photographers, Shutterstock is both a source of images and a monitoring tool for how those images are used.

Best Practices for Effective Image Searching
Want better and more accurate results? A few small tweaks can make a big difference.
1. Use High‑Quality Images
For visual and reverse searches:
-
Avoid blurry screenshots or tiny thumbnails
-
Use images where the main subject is clear and unobstructed
-
If needed, crop to focus on the main object, but don’t crop away too much detail
Low‑quality or heavily edited images can confuse algorithms and lead to weak matches.
2. Be Specific with Keywords
For keyword-based image search:
-
Swap vague terms like “shoes” for detailed phrases like “black leather men’s running shoes”
-
Include context if needed: “vector icon,” “transparent background,” “infographic,” etc.
The more specific and descriptive your query, the better the results.
3. Use Multiple Tools
Don’t rely on just one search engine.
-
Use Google for general coverage
-
Use TinEye for duplicates and origin tracking
-
Use Pinterest Lens for inspiration
-
Use Lenso AI for face‑related or misuse checks
-
Use Yandex when you need deeper or more global matches
Each tool has its strengths, and combining them gives you a fuller picture.
4. Apply Filters to Narrow Results
Most platforms let you filter by:
-
Image size
-
Color
-
Type (photo, illustration, icon, etc.)
-
Date
-
Usage rights
Filters are your best friend when you want images that are both relevant and legally usable.
5. Respect Copyright and Licensing
Always check:
-
Usage rights
-
Licensing terms
-
Attribution requirements
Using images without permission can lead to legal trouble and damage your reputation. Ethical image search isn’t just about finding content — it’s about using it responsibly.
Common Image Search Mistakes to Avoid
A few common errors can ruin your results or cause problems down the line. Here’s what to watch out for.
-
Using very poor or heavily edited images as your starting point
Over‑cropped, distorted, or filtered images are harder to recognize accurately. -
Relying on a single engine
You miss a lot if you never cross‑check on another tool. -
Ignoring filters and search options
This often leaves you scrolling through tons of irrelevant content. -
Skipping copyright checks
Grabbing the first image you like without checking its rights can backfire. -
Overloading your keyword queries
Long, messy keyword strings can confuse the engine. Clear, focused phrases usually perform better.
Keeping your queries simple, specific, and thoughtful will dramatically improve your image search experience.
Practical Applications of Image Search
Image search isn’t just for curiosity. It plays a serious role across many industries.
1. Journalism & Media Verification
Journalists use image search to:
-
Confirm whether a photo is genuine
-
Check if an image is old but being shared as “new”
-
See if a photo has been used in different, unrelated stories
This helps combat fake news and misinformation.
2. eCommerce & Online Shopping
Businesses and marketplaces use visual search to:
-
Let users upload a photo to find matching or similar products
-
Make product discovery more intuitive and visual
-
Increase conversion rates by reducing friction in the search process
Buyers can jump straight from “I like how this looks” to “Here’s where I can get it.”
3. Design & Creative Work
Designers, photographers, and marketers rely on image search to:
-
Find inspiration and references
-
Explore styles, color schemes, and patterns
-
Ensure consistency across brand assets
-
Check if ideas or visuals are already overused
It’s a key tool in both creative brainstorming and brand protection.
4. Education & Research
Teachers and students use image search to:
-
Find visual aids, charts, and illustrations
-
Verify sources and context of images used in assignments
-
Support presentations and projects with relevant visuals
It helps build more engaging and credible educational material.
5. Law Enforcement & Security
Authorities use facial and object recognition (where legally allowed) to:
-
Identify suspects or missing persons
-
Track stolen goods or counterfeit products
-
Connect visual evidence across different cases
Visual search plays a serious role in modern investigations.
6. Marketing & Brand Protection
Companies use image search to:
-
Monitor where their logos and brand visuals appear online
-
Detect unauthorized usage of campaigns or photography
-
Measure how far a visual campaign has spread
This helps protect brand integrity and maintain consistent messaging.
7. Social Media Monitoring
Creators and influencers use image search to:
-
Spot reposts and uncredited use of their content
-
Track collaborations and UGC (user‑generated content)
-
Understand how and where their visuals travel across platforms
It’s a powerful way to stay in control of your visual footprint.
The Future of Image Search
We’re still just getting started with what image search can do.
Here’s what’s coming next.
-
More accurate recognition
AI will get better at understanding not just objects but emotions, settings, and context. It will understand the “story” inside an image. -
Real‑time AR and wearable integration
Imagine pointing your phone or smart glasses at:-
A building and instantly seeing its history
-
A plant and getting its name and care instructions
-
A meal and seeing nutritional info and recipes
-
-
Smarter personalization
Visual search engines will learn your taste and intent, then tailor results to your preferences. -
Deeper understanding of edits and deepfakes
Tools will become more capable of spotting manipulated or AI‑generated content and flagging it accordingly. -
Greater focus on ethics and privacy
As facial recognition and visual tracking grow more powerful, discussions around privacy, consent, and regulation will become even more important.
The end goal is a world where you can interact with the visual web as naturally as you already do with text — but in a way that remains ethical, transparent, and trustworthy.
Summing Up
Image search techniques have completely changed how we navigate visual information online.
By learning how to use:
-
Keyword‑based image search
-
Reverse image search
-
Visual similarity search
-
Color and pattern‑based search
-
Object and facial recognition
you gain the ability to:
-
Verify what you see
-
Discover new products and ideas
-
Protect your creative work
-
Support research, design, and journalism
-
Stay safer and smarter in a visual‑first internet
Each method has its own strengths. The “right” one depends on whether you’re trying to research, design, shop, verify, or protect.
Conclusion
If the modern internet is a giant gallery of images, then image search techniques are your map, magnifying glass, and fact‑checker all rolled into one. They help you go beyond simply looking at pictures to actually understanding, validating, and using them wisely.
The more comfortable you get with these tools and methods, the more control you’ll have over the visuals you consume, share, and create — and that’s a real advantage in a world where what we see doesn’t always tell the full story.